The lines between reality and virtual worlds are blurring, thanks to the rapid adoption of mobile gaming, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) technologies. As these platforms evolve, they are not only changing how people play games but also reshaping how brands and advertisers can partner with gaming companies.
In our latest report, the Profiles team at Kantar shared insights into how global audiences consume media across devices and technologies. This research, spanning more than 10,000 global consumers, uncovered consumer gaming behaviour, including mobile and VR. Read more for a deep dive into how consumers are engaging with gaming.
The reign of mobile gaming
Mobile gaming has firmly established itself as the most popular form of gaming worldwide. Our latest report shows 69% of those who report to gaming regularly prefer using a phone or tablet for their gaming experiences over other devices like a tablet, computer or gaming console.

This preference is driven by the accessibility and convenience that mobile games offer. Whether it’s a quick puzzle game during a commute, Candy Crush while you’re waiting for a flight, or an extended session of a strategy game at home, mobile gaming easily fits into the daily lives of all kinds of players. The frequency with which games are played is also variable by type. Around 66% of mobile gamers report playing several times a week, with 31% engaging daily.
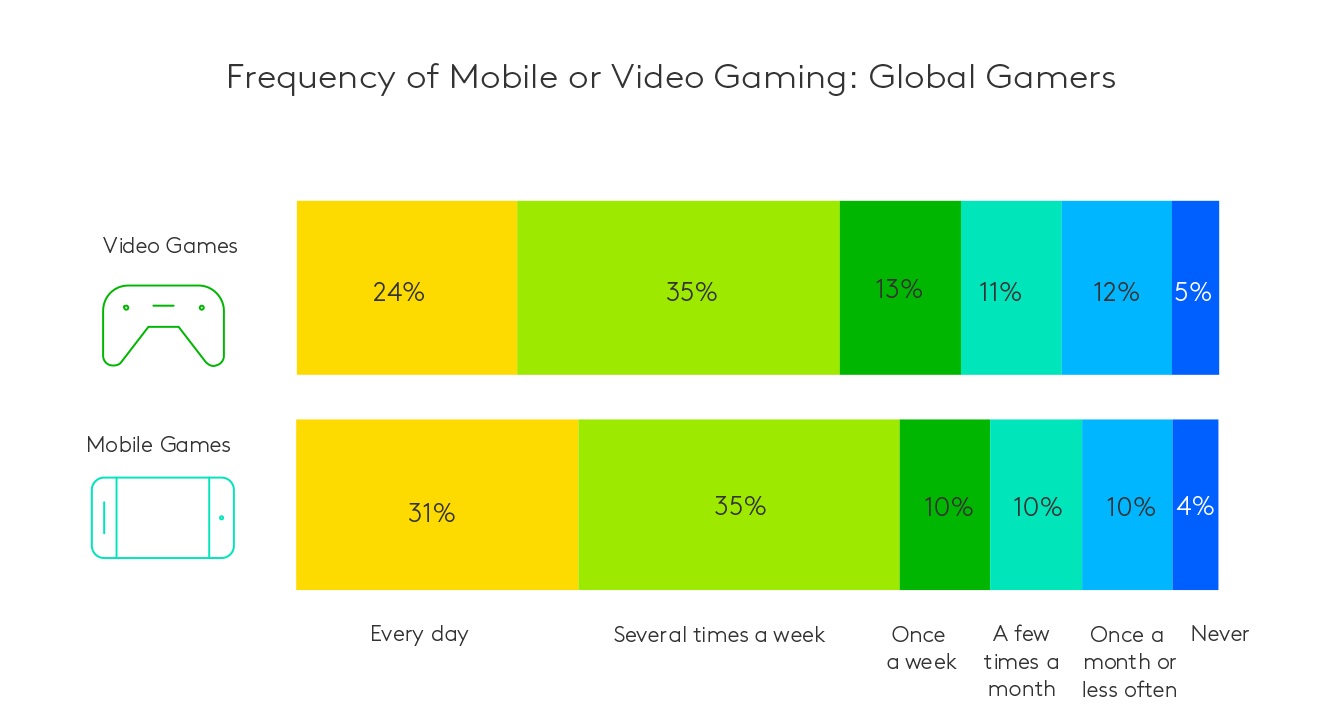
The growing appeal of VR in key markets
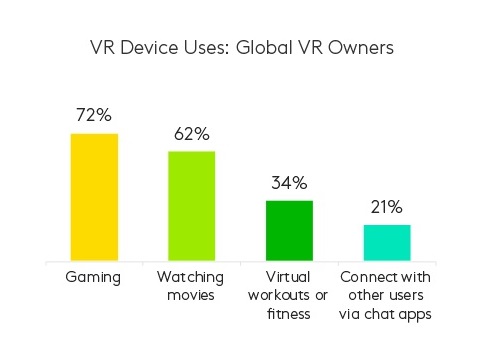
Virtual reality (VR), once a novelty technology, is gaining traction, particularly in countries like China (32%) and the United States (32%). In these regions, VR is becoming a more regular part of the gaming experience. Younger gamers are particularly drawn to VR, with those who own VR devices typically using them primarily for gaming.
The role of AR in enhancing gameplay
Augmented reality (AR) is another technology that is making waves in the gaming industry. AR overlays digital content onto the real world, creating a unique blend of virtual and physical experiences. Consumers view AR technology positively. Of those familiar with the technology, 75% consider it “innovative,” 84% find it “interesting,” and 78% say it is “engaging.” These perceptions highlight AR’s potential to enhance gaming experiences by making them more interactive and immersive.
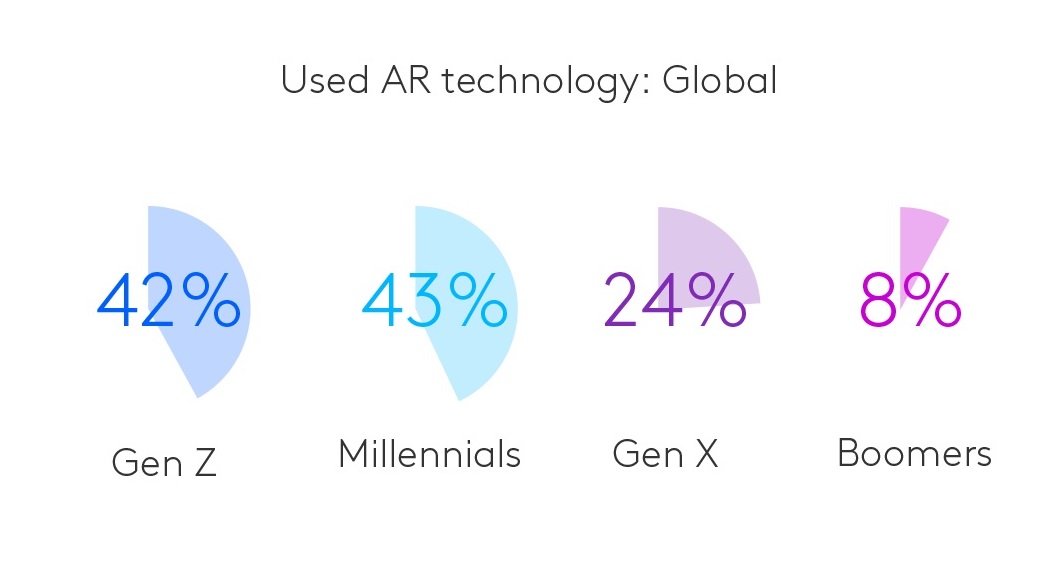
Younger audiences are more interested in using games that have an AR layer. Of those familiar with it, 42% of Gen Z and 43% of Millennials report having used AR, compared to 24% of Gen X and only 8% of Boomers. Mobile games like Pokémon Go have already demonstrated the appeal of AR, and as the technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of AR in gaming.
The power of incentives in gaming
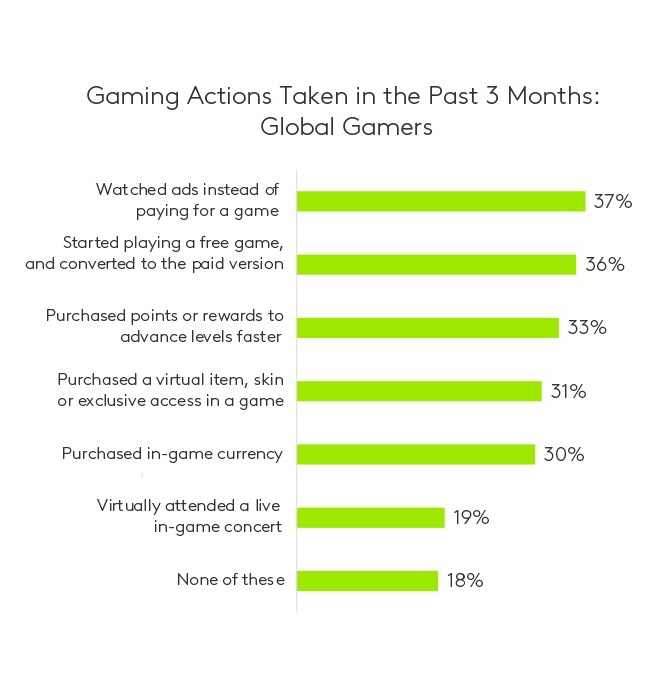
Gamers are highly responsive to incentives, according to this study, which could have significant implications for how games are monetised. Approximately 37% of regular gamers have watched ads to continue playing a free game, highlighting the willingness of players to engage with ads if it means uninterrupted gameplay. Additionally, 36% of regular gamers report they have converted from a free version to a paid version of a game, indicating that well-designed incentives can effectively drive revenue.
As gaming technologies continue to advance, mobile gaming is poised at the forefront of the category’s growth potential. Consumer interest in VR technologies are strong, indicating continued potential for growth as price points drop and devices become more accessible to consumers across markets. As these technologies advance, they will continue to shape the future of gaming, offering new and exciting ways for players to engage with the digital world.
Get more answers
For more findings from this study, access the complete Connecting with the Media & Entertainment Community report. Find additional insights into what global consumers are watching, playing and listening to.
About this study
This research was conducted online among more than 10,000 consumers across ten global markets (including Australia, Brazil, China, France, Germany, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, UK and US) between 27 May 2024 and 7 June, 2024. All interviews were conducted as online self-completion and collected based on controlled quotas evenly distributed between generations and gender by country. Respondents were sourced from the Kantar Profiles Respondent Hub.

